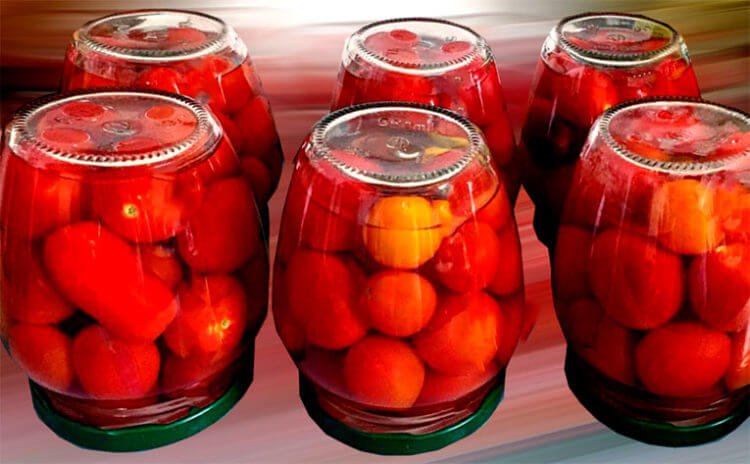
Tube pasteurizers
Tube-type pasteurizers are designed for rapid in-line pasteurization of milk in dairies, cheese and butter factories, as well as in canneries.
This unit is recommended for milk pasteurization in the production of warm milk, ryazhenka and cream, as well as in the production of butter by converting high-fat cream.
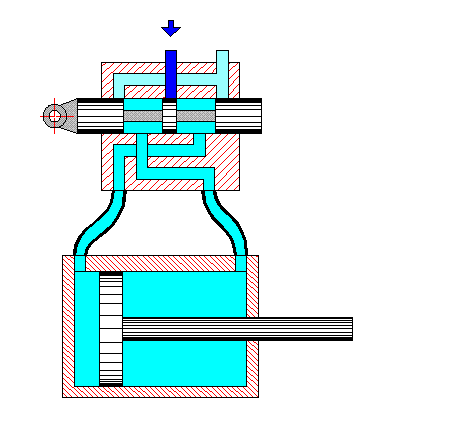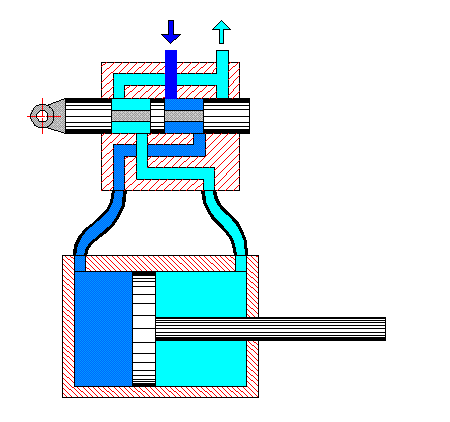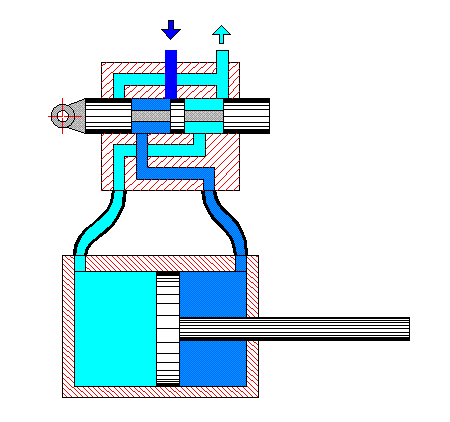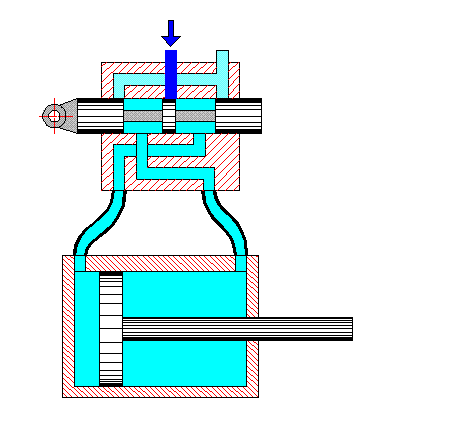
Raw milk is fed by a centrifugal pump (Fig. 1) into the pipes of the lower cylinder, where it is heated to 50 °C. The heated milk is fed by another centrifugal pump to the upper cylinder, where it is heated to 85-95 °C. A check valve located at the outlet of the machine cuts off unpasteurized milk and sends it for re-pasteurization, while the pasteurized milk is sent by the valve for further processing. 


Figure 2 - Tubular pasteurizer TI-OUK: a) - general view: 1 - lower cylinder; 2 - upper cylinder; 3 - condensate traps; 4 - milk pump; 5 and 6 - milk pipelines; 7 - steam pipeline;
b) - technological scheme: 1 and 2 - condensate traps; 3 - pump; 4 - milk pipelines; 5 - valve; 6 - technical pressure gauge.
The pasteurizer (Fig. 2) is designed for pasteurization of cream in butter production lines. It can also be used as a milk heater before separation (separators), for high-temperature pasteurization of milk in the production of melted milk and baked milk, as well as a cooler for milk and milk mixtures. When the pasteurizer is used as a cooler, cold water is supplied to the inter-tube space instead of the coolant.
The tubular pasteurizer consists of two cylinders: upper and lower. In each cylinder 24 pipes with a diameter of 27 mm are rolled. The pipes are connected in series, in pairs, by means of grooves milled in the pipe boards.
The coolant in the intertube space is steam, which is supplied in parallel to both cylinders. The liquid is pumped first into the first tube of the lower cylinder, then, after passing through all the tubes of the lower cylinder in sequence, it passes through the tubes of the upper cylinder in sequence. After passing through all 48 tubes of the upper and lower cylinders in sequence, the liquid leaves at t = 85-95 °C. Condensate formed in the intertube space is automatically removed from each cylinder by a condensate trap.